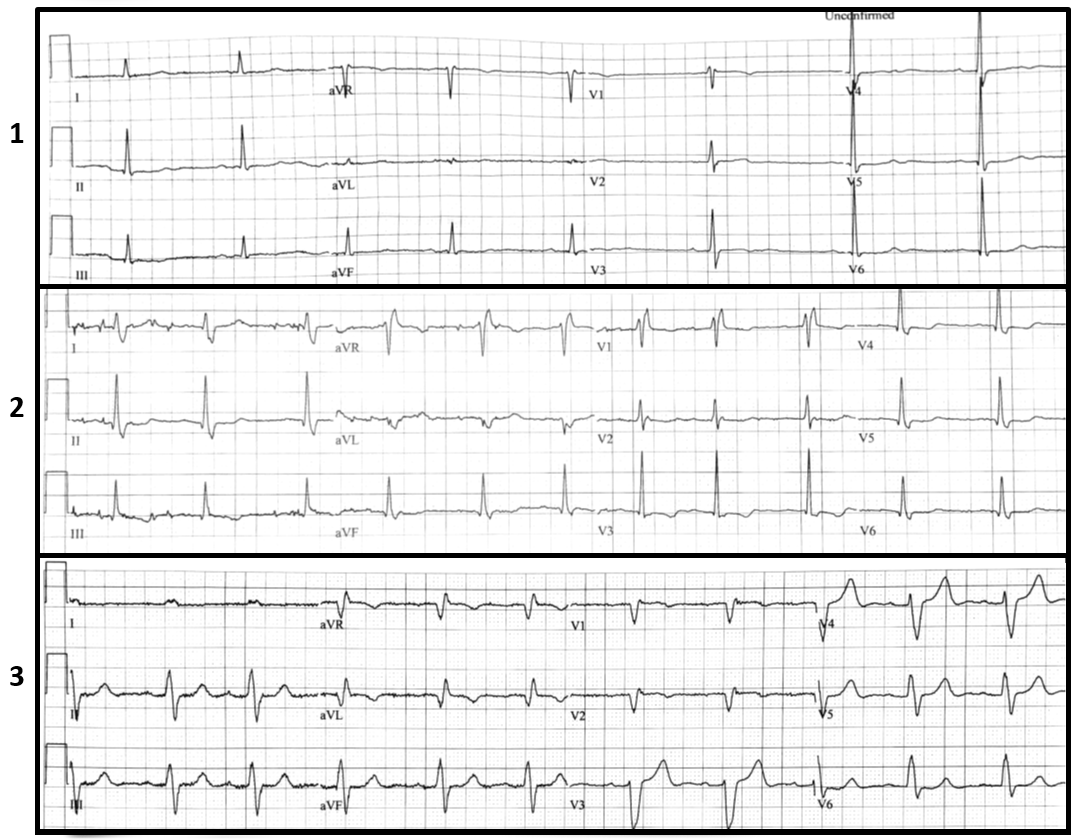
An 82-year-old woman with controlled hypertension presents with recurrent orthostatic lightheadedness without syncope. Her blood pressure and heart rate are 110/70 mm Hg and 60 beats per minute (bpm) while sitting, and 85/65 mm Hg and 65 bpm while standing for five minutes, respectively. Her physical exam, including a comprehensive cardiac exam, was unremarkable. On echocardiography she had a normal left ventricular ejection fraction and no significant valvular disease. The following electrocardiograms (ECGs) were obtained within few minutes of each other (Figure 1).
Figure 1
The correct answer is: A. Implant permanent pacemaker.
ECG #1 in Figure 1 shows sinus bradycardia with sinus arrhythmia at an average rate of 50 bpm with normal QRS duration. ECG #2 shows a right bundle branch block pattern at a faster sinus rate ~70 bpm ; and ECG #3 shows sinus rhythm at ~70 bpm with left bundle branch block and prolonged PR interval. Alternating bundle branch block is a class I indication for implantation of permanent pacemaker1 as it indicates diseased infranodal (hisian and infrahisian conduction disease), therefore further electrophysiology study is not needed for management. While her lightheadedness could be due to orthostatic hypotension, the patient, regardless of symptoms, required permanent pacemaker implantation.
References
- Tracy CM, Epstein AE, Marine JE, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/HRS focused update of the 2008 guidelines for device-based therapy of cardiac rhythm abnormalities: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2012;60:1297-1313.