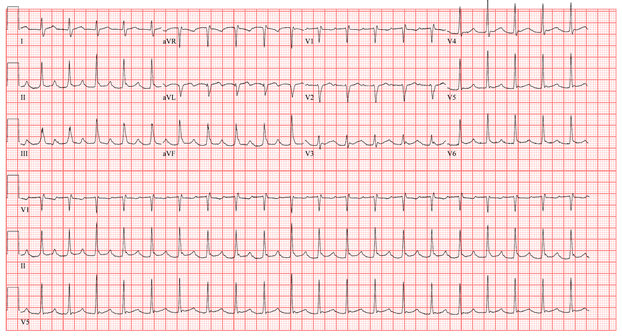
A 51-year-old man with a past medical history of myelodysplastic syndrome, chronic graft vs. host disease, status post allogeneic stem cell transplantation, non-obstructive coronary artery disease and pulmonary embolism presents to the emergency department with complaint of chest pain. Electrophysiology was consulted for an abnormal ECG, which is shown below.
The correct answer is: B. Atrial tachycardia
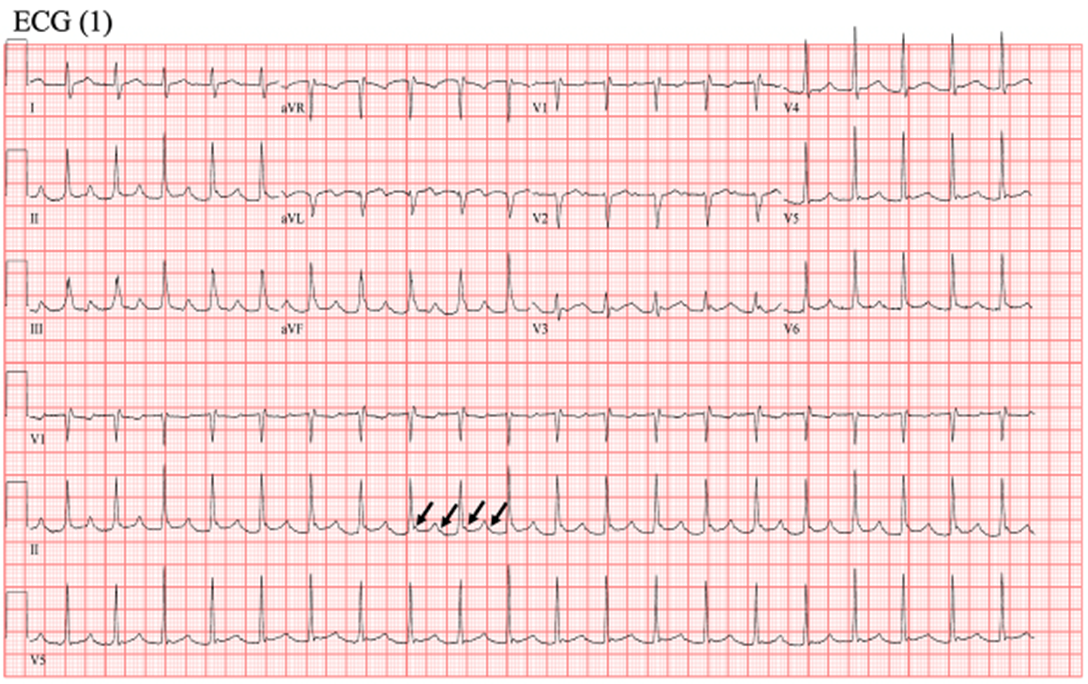
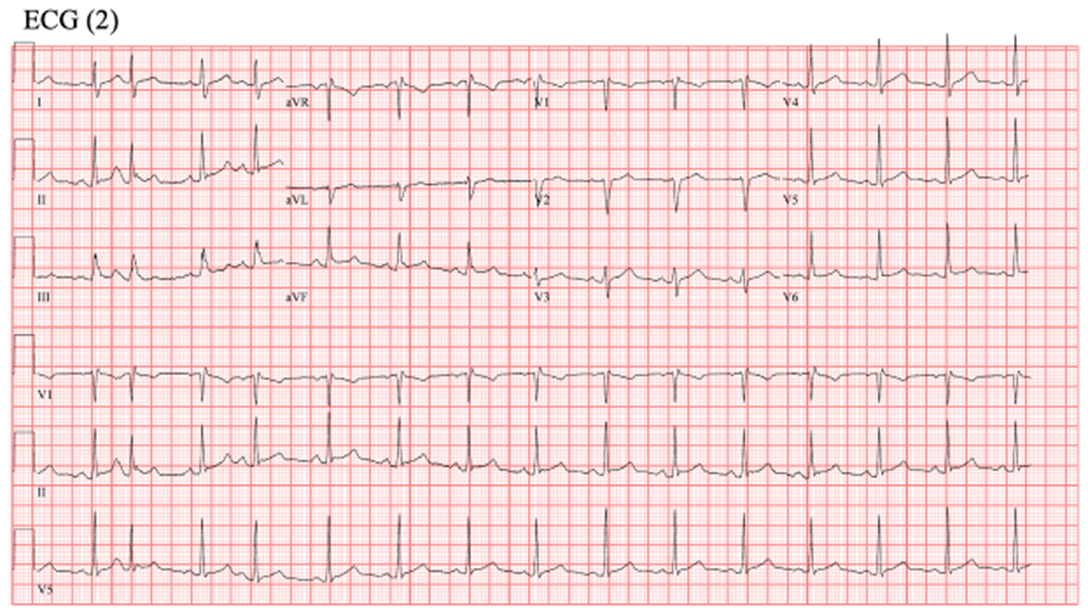
ECG (1) shows atrial tachycardia with 2:1 conduction. The black arrows depict the P waves that can be marched through the rhythm strips. The atrial rate is about 240 beat per minute with 2:1 AV conduction. On comparison with baseline ECG (2) when the patient is in sinus rhythm, the P wave morphology is different, and the P-R interval is shorter during sinus rhythm. There is isoelectric baseline between the two P waves, ruling out atrial flutter. The presence of P waves that march out eliminates junctional tachycardia as a diagnosis.
References
- Roberts-Thomson KC, Kistler PM, Kalman JM. Focal atrial tachycardia I: clinical features, diagnosis, mechanisms, and anatomic location. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2006;29:643-52.