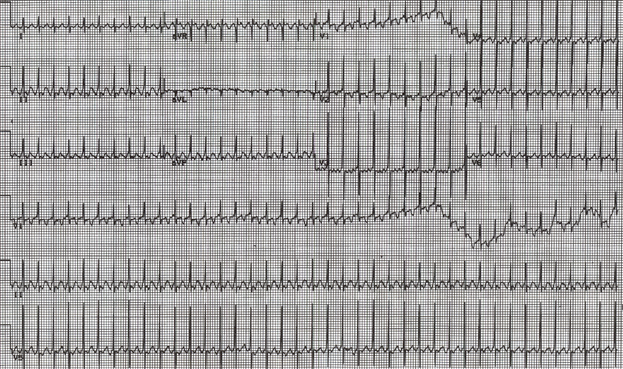
Performing synchronized electrical cardioversion would be the most appropriate next treatment to terminate the tachycardia. The 12-lead ECG tracing (Image 1) demonstrates tachycardia with narrow QRS complexes suggestive of either atrioventricular (AV) re-entrant tachycardia or atrial tachycardia. Close examination of the ECG tracing (especially leads II, V5, and V6) reveals two distinct, sharp, and inverted P waves between every QRS complex (Figure 1). Therefore, the ECG findings were most consistent with atrial flutter (AFL) with a classic sawtooth flutter wave pattern and 2:1 AV conduction.1
Figure 1: ECG Lead II During Tachycardia

ECG lead II during tachycardia highlighting the presence of two distinct, sharp, and inverted P waves (red arrows) between every QRS complex.
ECG = electrocardiogram.
If not treated promptly, sustained AFL with a rapid ventricular response rate can eventually lead to hemodynamic deterioration including tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy.2 Therefore, the primary goal is restoration of sinus rhythm. In infants with AFL, synchronized electrical cardioversion starting at 1 J/kg is highly effective in rapidly restoring sinus rhythm.2 Although transesophageal atrial overdrive pacing is a safe method to terminate AFL, the success rates are lower than for synchronized cardioversion secondary to challenges in achieving atrial capture at the rapid pacing rates required.3 Similarly, medications in this scenario are less effective than electrical cardioversion.2
Intravenous adenosine can effectively terminate atrioventricular node (AVN)–dependent re-entrant tachycardias; however, it would not terminate AFL because the re-entry circuit does not include the AVN.4 Adenosine, like vagal maneuvers, may unmask AFL on the ECG by transiently inhibiting AVN conduction, thereby making the flutter P waves more conspicuous between the more widely spaced QRS complexes (Image 2). Once inhibition of AVN conduction wears off, AFL with 2:1 AV conduction would resume.
Image 2: ECG During AFL After IV Adenosine Administration

The adenosine blocks AV conduction, which makes the AFL P waves easier to see.
AFL = atrial flutter; AV = atrioventricular; IV = intravenous.
The use of enteral beta-blocker therapy would not be appropriate for this patient. Beta-blockers can slow AVN conduction and thereby decrease the ventricular rate response in patients with AFL, but they do not convert AFL to sinus rhythm.5 With electrical defibrillation, the shock delivery is not synchronized to the QRS complexes. This is not recommended in AFL because the shock could inadvertently convert the rhythm to hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF) if the shock is delivered near the peak of the T wave. Rather, defibrillation should be reserved for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia such as VF or pulseless VT.6
In infants with AFL, synchronized cardioversion is the most effective strategy for restoring normal sinus rhythm (NSR). Studies have demonstrated that, once in sinus rhythm, infants without concomitant cardiac disease such as congenital heart defects, cardiomyopathy, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, or other atrial arrhythmia have an excellent long-term recurrence-free prognosis and may not require chronic antiarrhythmic therapy.7
This patient underwent successful synchronized cardioversion to sinus rhythm. His 12-lead-ECG in NSR did not have findings of ventricular pre-excitation. Given the absence of an additional arrhythmia substrate or structural heart disease, an antiarrhythmic medication was not prescribed. Over the 2 years of follow-up thus far, he has not had recurrence of AFL.
References
- Wójtowicz-Marzec M, Wysokińska B, Respondek-Liberska M. Successful treatment of neonatal atrial flutter by synchronized cardioversion: case report and literature review. BMC Pediatr. 2020;20(1):370. Published 2020 Aug 5. doi:10.1186/s12887-020-02259-7
- Kim G, Shin JH, Gang MH, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of atrial flutter in neonates. Pediatr Int. 2023;65(1):e15714. doi:10.1111/ped.15714
- Aljohani OA, Perry JC, Williams MR. Intravenous sotalol for conversion of atrial flutter in infants. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2018;4(3):117-120. Published 2018 Jan 10. doi:10.1016/j.hrcr.2018.01.002
- Zeytin A, Konca Ç, Varan C. Efficacy of adenosine in the differential diagnosis of narrow QRS complex tachyarrhythmia: a case diagnosed with atrial flutter after adenosine. J Pediatr Emerg Intensive Care Med. 2023 Aug;10(2):143-146. doi:10.4274/cayd.galenos.2022.17136
- Oka S, Kai T, Hoshino K, et al. Rate versus rhythm control in tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy patients with persistent atrial flutter. Int Heart J. 2021;62(1):119-126. doi:10.1536/ihj.20-266
- American Heart Association. Algorithms: 2025 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (AHA CPR & First Aid: Emergency Cardiovascular Care website). Available at: https://cpr.heart.org/en/resuscitation-science/cpr-and-ecc-guidelines/algorithms. Accessed 11/12/2025.
- Casey FA, McCrindle BW, Hamilton RM, Gow RM. Neonatal atrial flutter: significant early morbidity and excellent long-term prognosis. Am Heart J. 1997;133(3):302-306. doi:10.1016/s0002-8703(97)70224-2