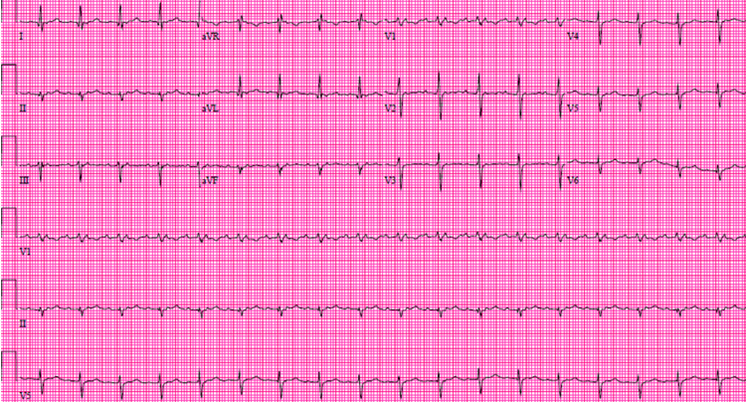
A 66-year-old male presents with increased fatigue and palpitations over the past few days. He has a history of hyperlipidemia, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and atrial fibrillation. An atrial fibrillation ablation procedure was recently performed. An ECG is performed (Figure 1).
Figure 1
The correct answer is: F. B and D.
The patient demonstrates a supraventricular tachycardia with 2:1 AV block. There is an isoelectric interval between the two P wave which rules out atrial flutter. P wave axis and morphology confirmed origin of the atrial tachycardia from the left upper lateral wall of the left atrium (Negative P wave in aVL and positive p wave in II and III). The P wave in the ST segment gives a pseudo right intra-ventricular conduction delay appearance. The QRS axis is -45 degree with initial Q waves in lead I and aVL, confirming left anterior fascicular block. The ectopic atrial tachycardia is an occasional occurrence after atrial fibrillation ablation. It is important to keep in mind that ectopic atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block is seen in digitalis toxicity. This patient was not on digoxin.
References
- Tang BS, Scheinman MM, Van Hare GF, Epstein LM, Fitzpatrick AP,Lee RJ. Use of P wave configuration during atrial tachycardia to predict site of origin. JACC 1995;26:1315-24.
- Chae S, Oral H, Good E, Dey S et al. Atrial tachycardia after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation of atrial fibrillation. JACC 2007;50:1781-7.