Poll: Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement in a High Surgical Risk Patient With Mitral Stenosis
Mrs. M is an 81-year-old female patient who presents with worsening exertional dyspnea. She has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, and prior surgical aortic valve replacement in the setting of severe symptomatic aortic stenosis.
She was diagnosed with severe mitral stenosis (Image 1a) due to mitral annular calcification (MAC) (Image 1b) with a mean gradient of 10 mm Hg (Image 1c) and moderate pulmonary hypertension (pulmonary artery systolic pressure 45 mm Hg). Due to high surgical risk (Society of Thoracic Surgeons score >8%),1 transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) in MAC was planned.2 To ensure procedural success, transcatheter heart valve (THV) sizing was performed using multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) and the residual area of the left ventricular outflow tract (neoLVOT) was measured using virtual THV modeling (Image 2).
Image 1a: A three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiogram again demonstrates severe mitral annular calcification with severe mitral leaflet restriction in diastole
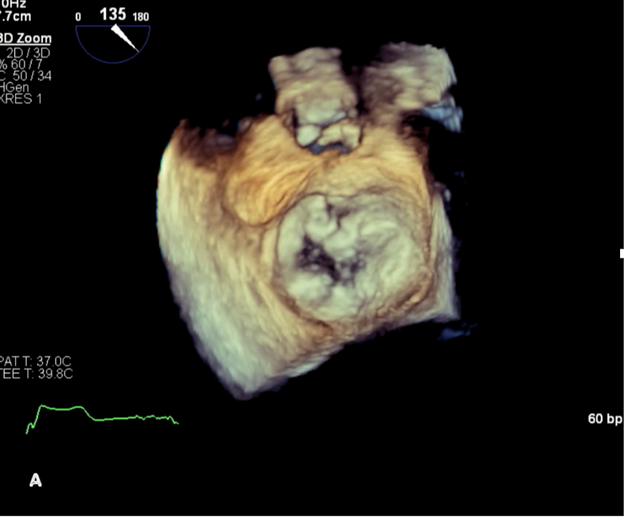
Image 1b: Multidetector computed tomography demonstrates nearly circumferential severe mitral annular calcification
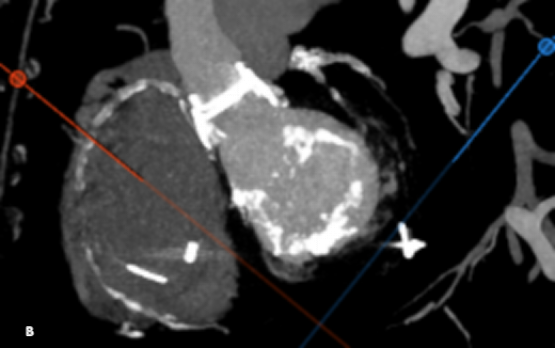
Image 1c: Transthoracic echocardiogram reveals a mean transmitral gradient of 10 mm Hg at a heart rate of 73 bpm
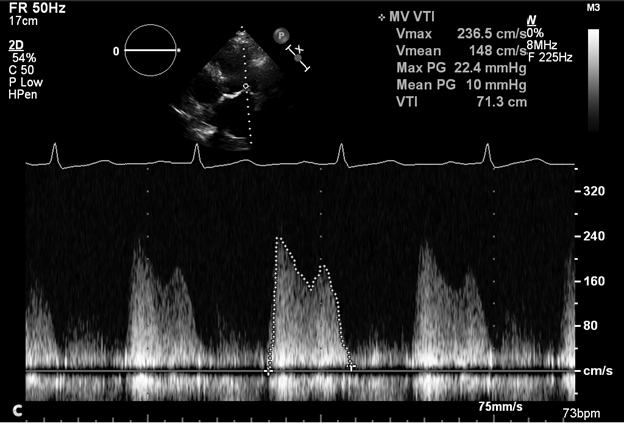
Image 2: Virtual transcatheter heart valve simulation to evaluate residual area of the left ventricular outflow tract (neoLVOT) and risk of LVOT obstruction on multidetector computed tomography
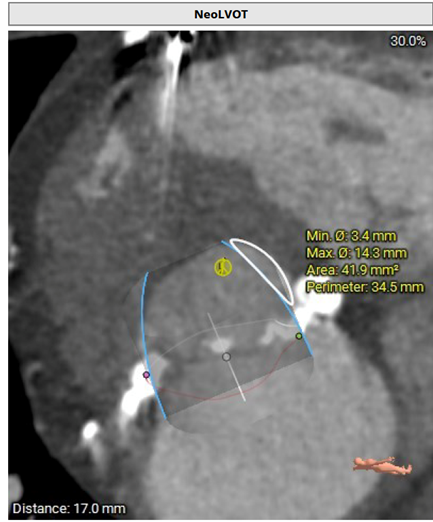
The neoLVOT area was found to be too small to support proceeding with TMVR in MAC due to an elevated risk of LVOT obstruction after the procedure.3
References
- Hemmann K, Sirotina M, De Rosa S, et al. The STS score is the strongest predictor of long-term survival following transcatheter aortic valve implantation, whereas access route (transapical versus transfemoral) has no predictive value beyond the periprocedural phase. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;17(2):359-364. doi:10.1093/icvts/ivt132
- Eleid MF, Wang DD, Pursnani A, et al. 2-year outcomes of transcatheter mitral valve replacement in patients with annular calcification, rings, and bioprostheses. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;80(23):2171-2183. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2022.09.037
- Reid A, Ben Zekry S, Turaga M, et al. Neo-LVOT and transcatheter mitral valve replacement: expert recommendations. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;14(4):854-866. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.09.027
Clinical Topics: Invasive Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention, Noninvasive Imaging, Valvular Heart Disease, Interventions and Imaging, Interventions and Structural Heart Disease, Computed Tomography, Nuclear Imaging, Cardiac Surgery, Cardiovascular Care Team
Keywords: Mitral Valve Stenosis, Multidetector Computed Tomography, Ventricular Outflow Obstruction