Amyloidosis Forum: Imaging Endpoints in AL and ATTR Amyloidosis Clinical Trials
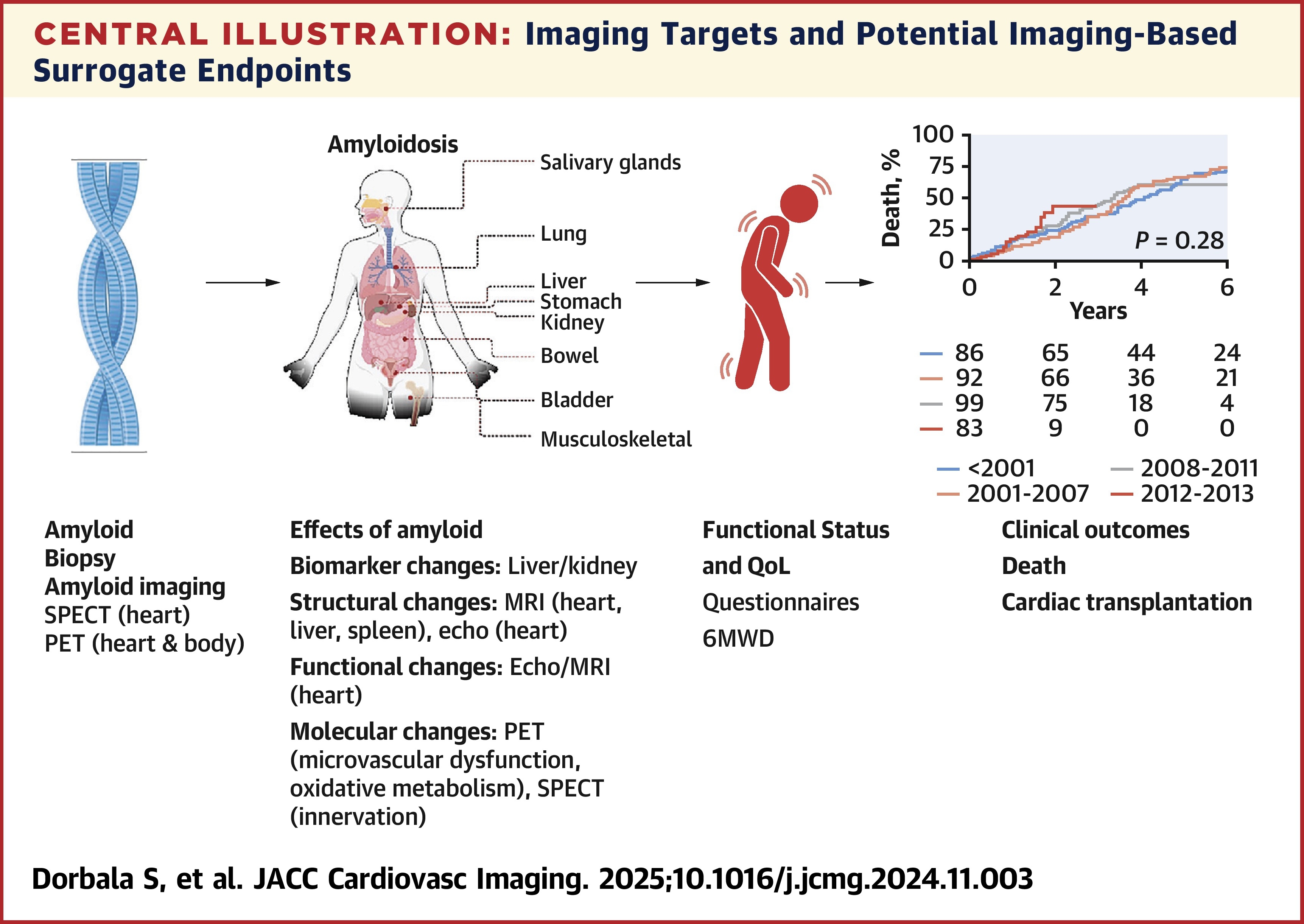
A new state-of-the-art review published March 5 in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging summarizes a discussion by the Amyloidosis Forum on the role of imaging biomarkers as trial endpoints in the diagnosis and assessment of systemic immunoglobin light chain (AL) and transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis.
The Amyloidosis Forum, a collaboration between the Amyloidosis Research Consortium and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, held a meeting to discuss the potential for imaging biomarkers to detect organ amyloid deposition, capture changes in cardiac function, select patients and guide therapy. The stated goal was to: "identify the activities required over the next 5 to 10 years to enable regulatory decisions based on imaging/composite endpoints, with a focus on patient-focused drug development in AL and ATTR amyloidosis."
The Forum focused on four modalities specifically: left ventricular longitudinal strain assessed by speckle tracking echocardiography, cardiac magnetic resonance-derived extracellular volume fraction mapping, bone-avid tracer cardiac single-photon emission computed-tomography (SPECT) and SPECT-CT, and positron emission tomography. While each modality has its strengths, the Forum also focused on current limitations, including the lack of standardized protocols and paucity of data from multicenter, long-term studies.
To incorporate patient-centered perspectives, the Forum examined survey results, finding that patients preferred imaging to biopsies and placed the highest important on being able to "see" the impact of treatment and the use of imaging in understanding disease status.
Panelists from the FDA, Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) spoke on what each of their organizations is doing to study the use of imaging as a primary endpoint, and the obstacles they are encountering while establishing the correlation between imaging markers and clinical benefit.
"With additional standardization, imaging has the potential to become a powerful tool to delineate efficacy of drug therapy, durability of treatment response, and optimal treatment duration in the case of anti-amyloid therapies," concludes the Forum. "Establishing rigor, reproducibility, and accuracy of imaging modalities is paramount to assess cardiac structural and functional changes and amyloid load for use in pivotal multicenter trials."
Clinical Topics: Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies, Invasive Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention, Noninvasive Imaging, Interventions and Imaging, Computed Tomography, Echocardiography/Ultrasound, Nuclear Imaging
Keywords: Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Biomarkers, Echocardiography, Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Computed Tomography, Tomography, Emission-Computed, Single-Photon, Amyloid Neuropathies, Familial, Amyloidosis, Familial, Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography, Tomography, X-Ray Computed, United States Food and Drug Administration
< Back to Listings
