Case 1: 76% of the audience got this wrong.
A 26 year old woman with a history of asthma requiring steroid treatment presents to the ER with sustained palpitations, dyspnea, and chest tightness. Her blood pressure is 110/75 mmHg. She looks uncomfortable and is tachycardic but the exam is otherwise unremarkable. Her ECG is shown above. CSM has no effect.
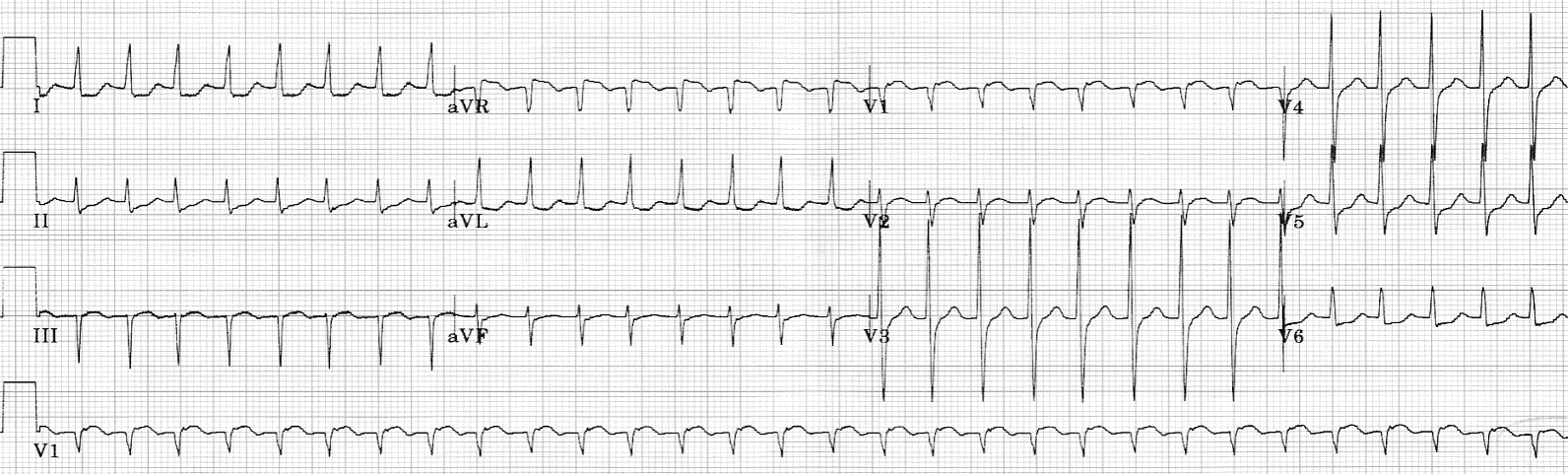
What is the most appropriate next treatment?
A. IV adenosine
B. IV magnesium
C. Synchronized electrical cardioversion
D. Oral digoxin load
E. IV verapamil
Correct Answer: E
Rationale:
The ECG shows a regular SVT with pseudo-R’ in V1 and pseudo S-waves in inferior leads. Class I options for medical termination of PSVT include both IV adenosine and IV verapamil, and the 2 medication are roughly similar in efficacy. However, adenosine is relatively contraindicated due to significant history of asthma requiring steroid treatment, as adenosine may provoke bronchospasm. IV verapamil is therefore the better choice. Oral digoxin is unlikely to be effective in PSVT termination in a reasonable time period. Magnesium is not effective for PSVT. Electrical cardioversion would be effective, but is rarely necessary to terminate PSVT and should not be used in a stable patient before vagal maneuvers and medications have been tried.
References:
Delaney B, et al. The relative efficacy of adenosine versus verapamil for the termination of stable paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in adults: A meta-analysis.
Join the nation’s leading cardiologists, including Kim A. Eagle, MD, MACC and Patrick T. O’Gara, MD, MACC, from around the country for an engaging and comprehensive review in general cardiology.
Whether you are preparing for the ABIM Board Exams to certify or re-certify or just want a comprehensive review in general cardiology, the ACC Cardiovascular Overview and Board Review for Certification and Recertification course has what you need!
Don’t delay — learn more and take advantage of the lowest registration rates today.
