Heart Valve Collaboratory Framework For Post-TAVR TVF Imaging
The Heart Valve Collaboratory has proposed a framework to standardize best practices for using multimodality imaging in transcatheter valve failure (TVF) following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), in a State-of-the-Art Review published in JACC.
In the review, the multidisciplinary panel of experts discuss imaging modalities for diagnosing TVF, anatomical evaluation for reintervention, procedure planning and follow-up for TAVR, and redo-TAVR. While success rates for TAVR are high, "the number of repeat interventions is likely to increase with time as the current volume of one million global TAVR procedures expands," write authors Omar K. Khalique, MD, FACC, et al., driving the need for an imaging framework.
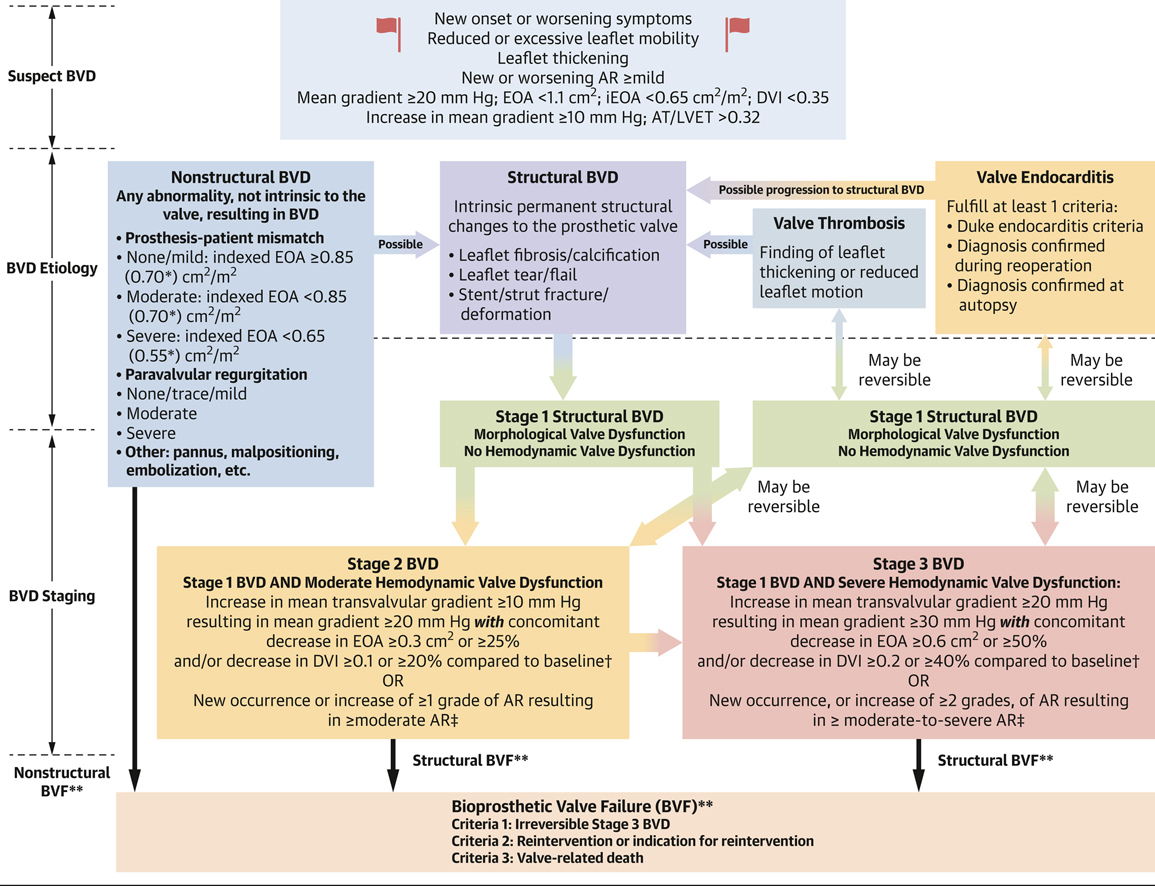
A core foundation emphasized is the need for precise definitions and staging criteria for bioprosthetic valve dysfunction (BVD) in all its forms. Nonstructural BVD includes prosthesis-patient mismatch, paravalvular leak, pannus and valve malpositioning. Structural BVD focuses on a permanent change to the leaflets or stent, while potentially reversible structural BVD includes cases of thrombosis and endocarditis. An algorithm to suspect, define and stage is provided, building on the initial Valve Academic Research Consortium-3/Heart Valve Collaboratory framework for BVF and its components.
For diagnosing TVF, recommendations are provided for systematic imaging in three settings: follow-up after TAVR, procedural planning for redo-TAV and after a redo-TAV. Imaging modalities discussed include echocardiography, cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA), cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and positron emission tomography (PET), as well as clinical situations where invasive assessment is needed. A case example illustrates imaging and decision-making for a patient being considered for redo-TAV.
Other topics discussed by the Collaboratory include imaging after the index TAVR using CCTA, CMR and PET/CT. For CT analysis before a re-do TAVR, they discuss, general principles and considerations, providing a table for a structured approach that outlines critical steps and measurements needed, as well as factors for selecting the type of re-do TAV and sizing and more.
The Redo TAV app can assist with this evaluation as it provides a patient-specific, combination-specific, step-by-step planning guide for CT analysis. Users can document data after the re-do TAV which can be integrated into the electronic medical record. More advanced software and simulations can visualize simple implantation and even provide a digital twin for more complex strategies.
Recognizing the need for more data to continue to refine parameters for decision-making, the authors note the value of establishing an imaging-centered redo-TAV registry. They write: "The relative importance of the specific imaging modalities and methodologies stated requires a concentrated collaborative effort for systematic validation in international multicenter prospective series and registries."
Clinical Topics: Cardiac Surgery, Cardiovascular Care Team, Invasive Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention, Noninvasive Imaging, Interventions and Imaging, Computed Tomography, Nuclear Imaging
Keywords: Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography, Computed Tomography, Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement, Computed Tomography Angiography, Positron-Emission Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Endocarditis, Thrombosis
< Back to Listings
