Can Lamin Dilated Cardiomyopathy Be Identified Earlier?
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging was able to detect longer myocardial T2, higher extracellular volume (ECV) fraction and worse myocardial dynamics, including impaired strain, before significant decline in left ventricular (LV) systolic function in carriers of LMNA (Lamin) dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Furthermore, the CMR-derived biomarkers of fibrosis (based on ECV) and strain are prognostic for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) during the disease's progression, according to a new study published in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
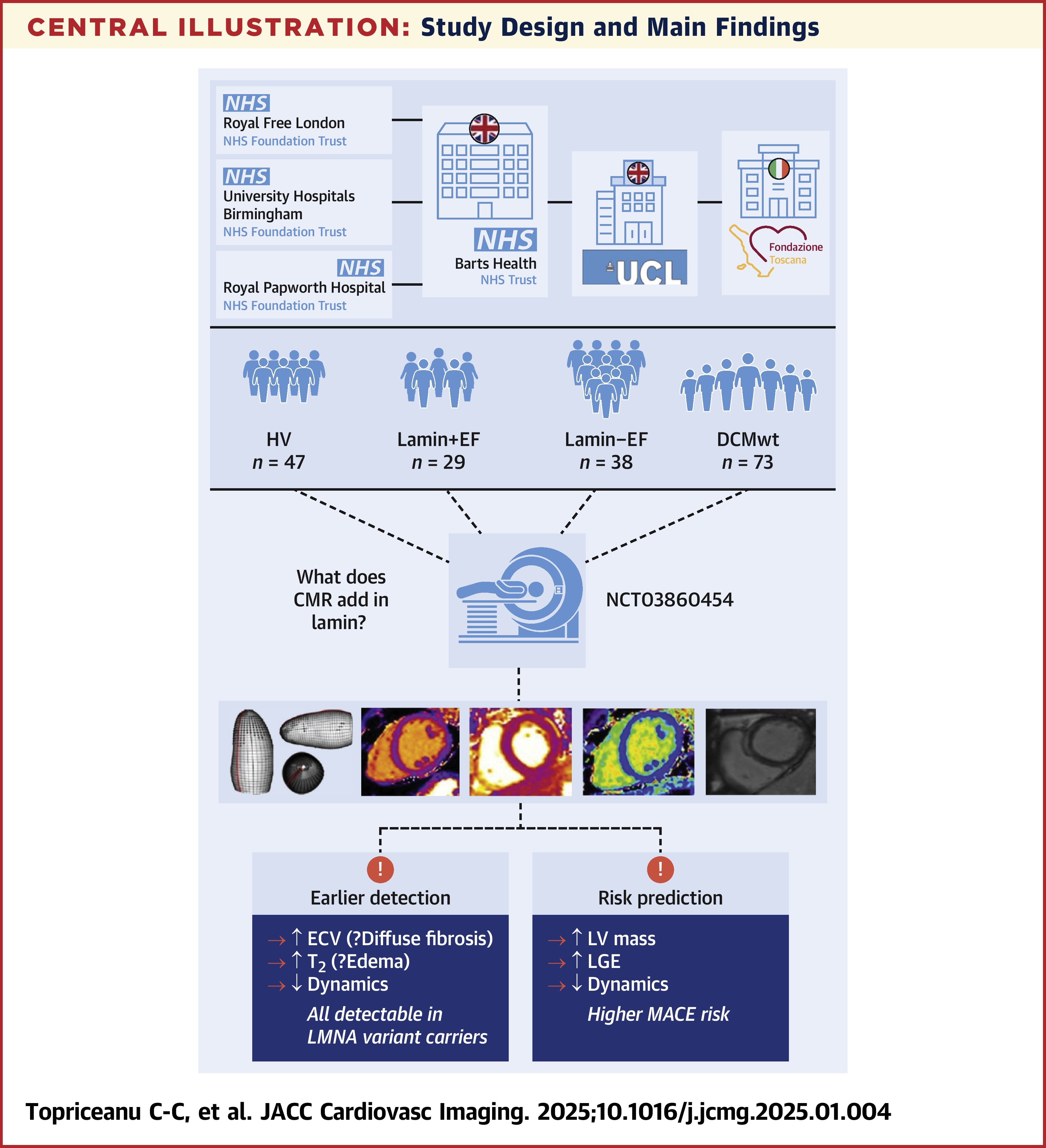
In the prospective, multicenter study, Constantin-Cristian Topriceanu, MD, et al., performed CMR (including late gadolinium enhancement [LGE] and 4D Procrustes motion analysis) and collected serum biomarkers (including NT-proBNP, C-reactive protein [CRP] and creatinine) on 187 individuals (50% women) in four groups: 1) 29 patients who carry pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) LMNA with LVEF ≥50% (Lamin+EF); 2) 38 patients who carry P/LP LMNA with LVEF <50% (Lamin-EF); 3) 73 patients with DCM with wild-type LMNA (DCMwt); and 4) 47 healthy volunteers. Those in the Lamin+EF group compared with the Lamin-EF group were younger (median age 38 years vs. 47 years), otherwise the groups were mostly similar.
The primary outcome to determine the prognostic potential was MACE, including cardiovascular death, life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmia, heart transplantation or atrioventricular block requiring pacing.
Results showed that the Lamin+EF arm had longer phantom-normalized T2 by 10, higher ECV fraction by 3% and worse myocardial dynamics compared to healthy volunteers. Compared to DCMwt participants, the Lamin+EF arm had better myocardial dynamics and higher levels of phantom-normalized T2 (20 vs. 12), serum troponin (27 ng/L vs. 5 ng/L) and C-reactive protein (8 mg/L vs. 3 mg/L).
Additionally, the Lamin-EF arm had similar myocardial dynamics, higher serum troponin (13 ng/L vs. 5 ng/L) and NT-proBNP (668 pg/mL vs. 228 pg/mL) levels, longer phantom-normalized T2 by 16 and higher ECV by 5% compared to the DCMwt arm.
At four years' follow-up, 21% of the lamin arms and 6% of the DCMwt arm had experienced MACE. Univariable Cox regression showed that in the lamin arms, each 1% increase in global LGE and each 1% decrease in Procrustes trajectory size was associated with increased hazard rates for MACE of 1.15 and 1.01, respectively.
The study authors champion the need for a revised risk calculator for LMNA carriers and posit that, "robust biomarkers that could predict phenotypic conversion from being a LMNA variant carrier to having overt lamin heart disease are desirable to guide outpatient follow-up strategies." They add that "LMNA variant carriers with normal systolic function have less adverse remodeling, meaning that this stage may be more amenable to disease-modifying therapies. This provides a window of opportunity to slow, or even halt, disease progression."
"The investigators provide compelling evidence for an early aggressive approach to evaluating LMNA carriers with CMR imaging," write Karolina M. Zareba, MD, and Ray Hershberger, MD, FACC, in an accompanying editorial comment. "Detection of the earliest myocardial tissue and dynamic alterations is key to improving outcomes in the high-risk LMNA population."
Clinical Topics: Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Dilated, Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Lamins, Disease Progression, Fibrosis
< Back to Listings
