New in Clinical Documents | HFpEF the Focus of New Clinical Guidance
With the incidence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) on the rise and accounting for more than 50% of all HF cases, a new ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway provides important guidance on the diagnosis and management of patients with the disease. Additionally, a JACC Scientific Statement further examines the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of HFpEF.
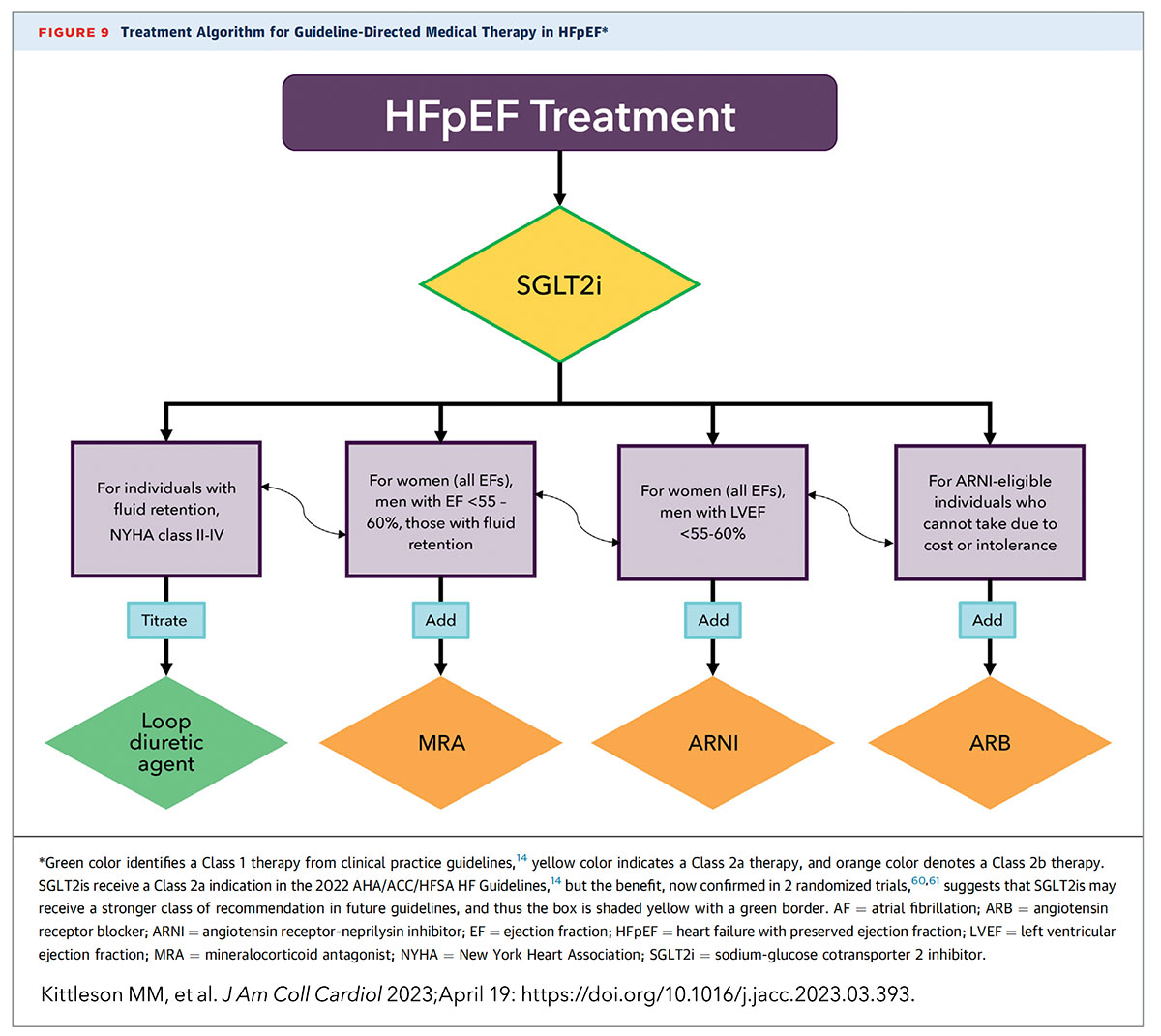
The 2023 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Management of HFpEF, published in JACC, incorporates emerging data from clinical trials and includes practical tips and tools to help clinicians with "timely identification and implementation of therapy" to improve patient outcomes. It specifically addresses diagnostic challenges tied to ejection fraction threshold, correct terminology, gender and sex differences, and the lack of a single test that definitively establishes diagnosis. In addition to diagnosis, the document offers insights into HFpEF therapeutic strategies using guideline-directed medical therapy (i.e., SGLT2 inhibitors) and other nonpharmacological tactics like exercise, caloric restriction and pulmonary artery pressure monitoring. It also provides guidance on managing comorbidities that contribute to symptoms and prognosis, including hypertension, obesity, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, sleep apnea and chronic kidney disease.
Multidisciplinary collaboration is also an important focus of the Pathway, with checklists provided to help clinicians determine when to refer patients to a cardiovascular specialist or an advanced heart failure specialist, as well as to help optimize communications among clinicians involved in continuing care. Essential skills for team-based care are also outlined and palliative care considerations are addressed.
"HFpEF is often under-recognized and results in substantial resource utilization," note Writing Committee Chair Michelle M. Kittleson, MD, PhD, FACC, and Vice Chair Gurusher S. Panjrath, MBBS, FACC, et al. "Historically, treatment options were limited to managing comorbidities; however, revolutionary advances in the past decade regarding the pathophysiology of HFpEF, improved methods of diagnosis, and insights into prognostic predictions now yield novel, effective management strategies. With recent favorable clinical trial results, there is increasing urgency for accurate diagnosis and timely implementation of GDMT."
The JACC Statement authored by Barry A. Borlaug, MD, FACC; Kavita Sharma, MD; Sanjiv J. Shah, MD, FACC; and Jennifer E. Ho, MD, FACC, further underscores the challenges associated with diagnosis and management of HFpEF.
"Despite recent advances in the understanding of its pathophysiological effects on the heart, lungs, and extracardiac tissues, and introduction of new, easily implemented approaches to diagnosis, HFpEF remains under-recognized in everyday practice," they write. "This under-recognition presents an even greater concern given the recent identification of highly effective pharmacologic-based and lifestyle-based treatments that can improve clinical status and reduce morbidity and mortality."
The statement highlights temporal disease progression in HFpEF and includes an overarching table of "clues to the possible presence of an HFpEF masquerader." It also summarizes key points for treatment of HFpEF, "with emphasis on evaluation and treatment of congestion with diuretics and SGLT2 inhibitors, treatment of comorbidities, lifestyle interventions, and vigilant consideration for HFpEF masqueraders that are treated differently." Additionally, a table outlining the large number of ongoing and upcoming clinical trials in HFpEF is incorporated.
"Ongoing large-scale studies of HFpEF pathobiology, an increasing number of translational studies spanning the gap between the bedside and the bench, and numerous clinical trials of novel therapeutics in HFpEF offer a glimpse of hope toward a future of reduced prevalence, morbidity, and mortality associated with HFpEF, which would be a major advance for population health," the authors say.
Clinical Topics: Acute Coronary Syndromes, Anticoagulation Management, Arrhythmias and Clinical EP, Diabetes and Cardiometabolic Disease, Dyslipidemia, Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies, Invasive Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention, Pericardial Disease, Prevention, Atherosclerotic Disease (CAD/PAD), Anticoagulation Management and ACS, Anticoagulation Management and Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Fibrillation/Supraventricular Arrhythmias, Lipid Metabolism, Acute Heart Failure, Interventions and ACS, Interventions and Coronary Artery Disease, Interventions and Imaging, Angiography, Nuclear Imaging, Exercise, Hypertension
Keywords: ACC Publications, Cardiology Magazine, Acute Coronary Syndrome, Heart Failure, Prognosis, Stroke Volume, Incidence, Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2, Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors, Coronary Artery Disease, Apnea, Atrial Fibrillation, Hypertension, Renal Insufficiency, Chronic, Diuretics, Disease Progression, Lung, Exercise, Fibrinolytic Agents, Pericardial Effusion, Follow-Up Studies, Thromboembolism, Thrombosis, Anticoagulants, Angiography
< Back to Listings


